Create ASP.NET MVC Controllers under Namespace and specific URL
When you have a lot of controllers, you need to organize them under Namespaces. Also, it is better to put controllers under subfolders in order to organize them properly and have some meaningful URL for them like /Admin/User where Admin is the subfolder and User is the controller. For example, you might have a lot of controllers that are APIs exposed by your web app, not regular pages. So, you might want to put them under /API/ folder. You also want to make sure no one can access those controllers from the root url. For example, no one must call /User/GetUserList instead they must call /API/User/GetUserList
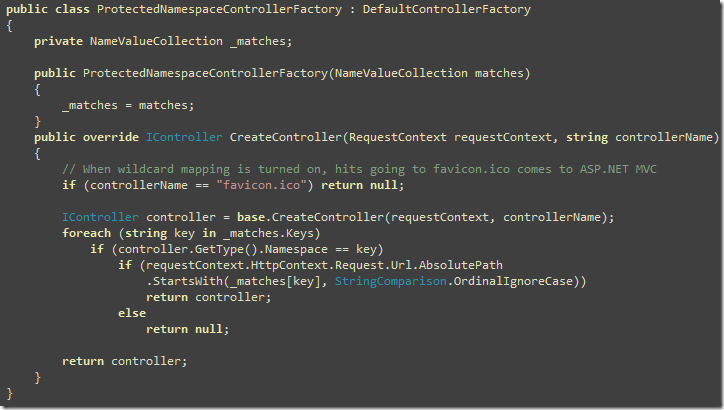
ASP.NET MVC default routing and Controller Factory is very greedy, it ignores the subfolders inside the "Controllers" folder. There's a DefaultControllerFactory class in ASP.NET MVC which traverses all controllers under the "Controller" folder and creates a cache using just the class name as the key. So, it ignores any namespace or any subfolder where you have put the controller. So, I created a derivative of the default controller factory and created a new factory that checks if the requested controller belongs to any specific namespace and whether that controller must be inside a specific subfolder. You can map /Admin folder to respond to all controllers that are under then YourWebApp.Admin namespace. Similarly, you can map /API folder to respond to all controllers that are under the YourWebApp.API namespace. None of these controllers can be accessed outside the specified URL. Here's the factory that does it:
This controller checks the namespace of the controller being returned by ASP.NET MVC's default implementation and ensures the requested URL is the right url where controllers from the namespace can be accessed. So, this means if the controller matches MvcWebAPI.API.UserController, it ensures the URL being requested must be /MvcWebAPI/API/User. It will return null if the URL was something else like /MvcWebAPI/User or /MvcWebAPI/SomeotherFolder/User.
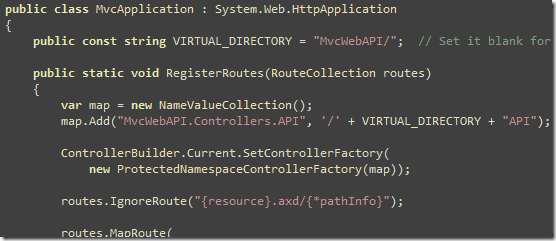
Here's how you use it form Global.asax:
You create a mapping for a Namespace and the subfolder it must belong to. Then you register the new Controller Factory as the default controller factory.
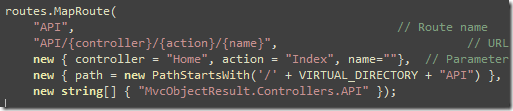
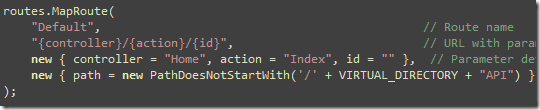
Now the second catch is, the default Route for the {controller}/{action}/{id} won't work for you. You need to create a specific router that starts with the subfolder name. For example, API/{controller}/{action}
Here' two things to notice:
- The use of PathStartWith routing constraint, which I will explain soon
- The last parameter which tells the route to include the API namespace for this route. Otherwise it can't find the controllers in the API namespace
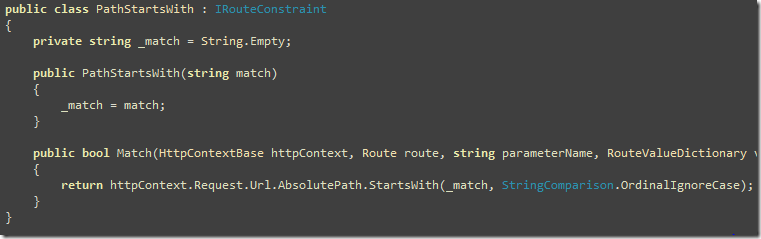
So, the PathStartsWith routing constraint ensures this route gets hit only when the requested URL is under the /API/ folder. For any other URL, it returns false and thus the routing handler skips this route.
It just does a comparison on the AbsolutePath of the current request URL to ensure the URL starts with the specified match.
Similarly, we need to tell the Default route to ignore all paths with /API. Here's how to do it:
That's it. Enjoy the full code from:
http://code.msdn.microsoft.com/MvcWebAPI
Read my previous post on creating Web API using ASP.NET MVC that can consume and expose Json and Xml:
Create REST API using ASP.NET MVC that speaks both Json and plain Xml
Note: incase you already read it, I have published new code that you should download.