NHibernate Mappings
In this post, I will talk about NHibernate mappings. Let's start from the data model:
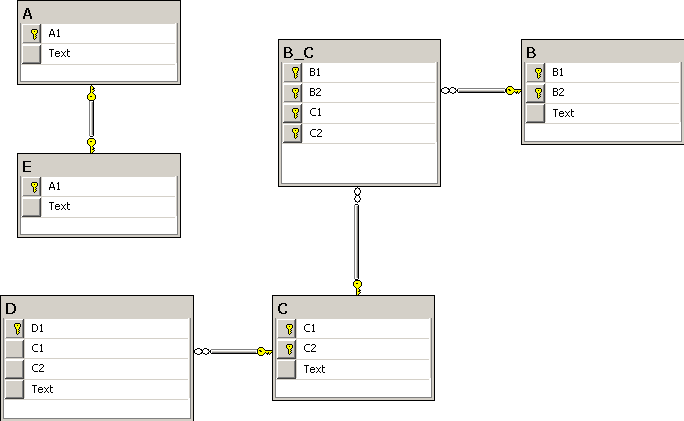
What we can see here are 4 types of relationships:
-
A one-to-one, from table A to table E;
-
A many-to-one, from table B to table C;
-
A one-to-many, from table C to table D;
-
A many-to-one, from table D to table C.
Also, note this:
-
All tables, except A, D and E, have composite primary keys; this is the most generic case;
-
All tables, except B_C, have a Text column;
-
Primary keys are always named <tablename><number>, for example, A1, A2, etc;
-
Foreign keys have the same name as the referring primary key.
Now, let's see the classes that map these tables and relationships:
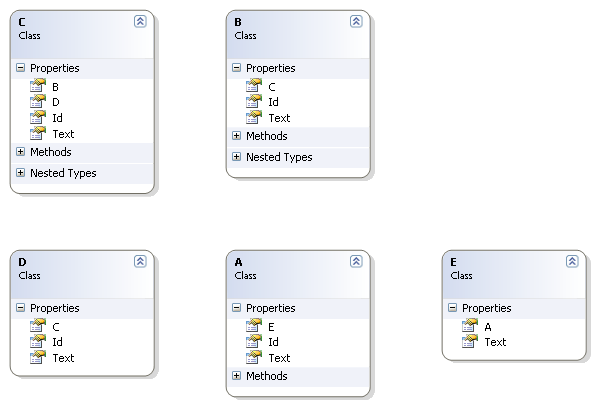
And the source code is:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace NHibernateTest{
[Serializable]public class A
{
public virtual Int32 Id { get; set; }
public virtual E E { get; set; }public virtual String Text { get; set; }
public override Boolean Equals(Object obj){
if (!(obj is A)){
return (false);}
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(this, obj) == true){
return (true);}
A other = obj as A;
return(this.Id == other.Id);}
public override Int32 GetHashCode(){
return (this.Id);}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace NHibernateTest{
[Serializable]public class B
{
public class BKey
{
public virtual Int32 B1 { get; set; }
public virtual Int32 B2 { get; set; }
public override Boolean Equals(Object obj){
if (!(obj is BKey)){
return (false);}
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(this, obj) == true){
return (true);}
BKey other = obj as BKey;
return ((this.B1 == other.B1) && (this.B2 == other.B2));}
public override Int32 GetHashCode(){
return (this.B1 + (1000 * this.B2));}
}
public virtual BKey Id { get; set; }
public virtual String Text { get; set; }public virtual ISet<C> C { get; set; }
public override Boolean Equals(Object obj){
if (!(obj is B)){
return (false);}
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(this, obj) == true){
return (true);}
B other = obj as B;
return (Object.Equals(this.Id, other.Id) == true);}
public override Int32 GetHashCode(){
return (this.Id != null ? this.Id.GetHashCode() : 0);}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace NHibernateTest{
[Serializable]public class C
{
public class CKey
{
public virtual Int32 C1 { get; set; }
public virtual Int32 C2 { get; set; }
public override Boolean Equals(Object obj){
if (!(obj is CKey)){
return (false);}
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(this, obj) == true){
return (true);}
CKey other = obj as CKey;
return ((this.C1 == other.C1) && (this.C2 == other.C2));}
public override Int32 GetHashCode(){
return (this.C1 + (1000 * this.C2));}
}
public virtual CKey Id { get; set; }
public virtual String Text { get; set; }public virtual ISet<B> B { get; set; }
public virtual ISet<D> D { get; set; }
public override Boolean Equals(Object obj){
if (!(obj is C)){
return (false);}
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(this, obj) == true){
return (true);}
C other = obj as C;
return (Object.Equals(this.Id, other.Id) == true);}
public override Int32 GetHashCode(){
return (this.Id != null ? this.Id.GetHashCode() : 0);}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace NHibernateTest{
[Serializable]public class D
{
public virtual Int32 Id { get; set; }
public virtual C C { get; set; }
public virtual String Text { get; set; }}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace NHibernateTest{
[Serializable]public class E
{
public virtual A A { get; set; }
public virtual String Text { get; set; }}
}
As you can see:
-
There is no class to map table B_C, this is because this is pure mapping table, it contains no additional attributes other than the foreign keys;
-
The id for class E is a property of type A;
-
No base class;
-
Methods Equals and GetHashCode are always implemented;
-
Collections are ISet<T>, which means they cannot hold equal objects;
-
Properties are auto properties and always have public setters;
-
Id classes for mapping composite keys are implemented as internal.
Now, here are the mappings:
For class A:
<hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2" namespace="NHibernateTest" assembly="NHibernateTest" auto-import="true" default-access="property"> <class name="A" table="`A`"><id name="Id" column="`A1`">
<generator class="foreign"><param name="property">E</param>
</generator></id>
<property name="Text" column="`TEXT`"/><one-to-one name="E" class="E" />
</class></hibernate-mapping>
For class B:
<hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2" namespace="NHibernateTest" assembly="NHibernateTest" auto-import="true" default-access="property"><class name="B" table="`B`">
<composite-id class="B+BKey" name="Id"><key-property column="`B1`" name="B1"/>
<key-property column="`B2`" name="B2"/> </composite-id><property name="Text" column="`TEXT`"/>
<set name="C" table="`B_C`" fetch="join" cascade="save-update" outer-join="true"><key>
<column name="`B1`"/><column name="`B2`"/>
</key><many-to-many class="C" fetch="join" outer-join="true">
<column name="`C1`"/><column name="`C2`"/>
</many-to-many></set>
</class></hibernate-mapping>
For class C:
<hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2" namespace="NHibernateTest" assembly="NHibernateTest" auto-import="true" default-access="property"><class name="C" table="`C`">
<composite-id class="C+CKey" name="Id"><key-property column="`C1`" name="C1"/>
<key-property column="`C2`" name="C2"/></composite-id>
<property name="Text" column="`TEXT`" /><set name="B" table="`B_C`" fetch="join" cascade="save-update" outer-join="true">
<key><column name="`C1`"/>
<column name="`C2`"/></key>
<many-to-many class="B" fetch="join"> <column name="`B1`"/><column name="`B2`"/>
</many-to-many></set>
<set name="D" inverse="true" cascade="all-delete-orphan" outer-join="true"><key>
<column name="`C1`"/><column name="`C2`"/>
</key><one-to-many class="D"/>
</set></class>
</hibernate-mapping>For class D:
<hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2" namespace="NHibernateTest" assembly="NHibernateTest" auto-import="true" default-access="property"><class name="D" table="`D`">
<id name="Id" column="`D1`"><generator class="assigned"/>
</id><property name="Text" column="`TEXT`"/>
<many-to-one name="C"><column name="`C1`"/>
<column name="`C2`"/></many-to-one>
</class></hibernate-mapping>
And finally, for class E:
<hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2" namespace="NHibernateTest" assembly="NHibernateTest" auto-import="true" default-access="property"><class name="E" table="`E`">
<id type="System.Int32"><column name="`A1`"/>
<generator class="assigned"/></id>
<one-to-one name="A" class="A"/><property name="Text" column="`TEXT`"/>
</class></hibernate-mapping>
The notes for the mappings are:
- Table and column names are enclosed in `;
- Collections are sets, not lists, idbags or bags;
- Primary keys are manually assigned;
- Properties are directly used to access values;
- Collections always use outer-join.
Hope this is useful to somebody!