DotNetStories


This is going to be the third post of a series of posts regarding ASP.Net and the Entity Framework and how we can use Entity Framework to access our datastore. You can find the first one here and the second one here.
I have a post regarding ASP.Net and EntityDataSource. You can read it here.I have 3 more posts on Profiling Entity Framework applications. You can have a look at them here,here and here.
In this post I will show you how to select,insert,update,delete data in the database using EF and stored procs. A lot of people use stored procedures when they use EF so they know exactly what hits their database.
I will be using Entity Framework version 4.0 that ships with Visual Studio 2010 and .Net 4.0.
In this very first post we will create a simple website and use Entity Framework as our data access layer.
I assume that you have access to a version of SQL Server.If you do not, you can download and install the free SQL Server Express edition from here.
1) Launch Visual Studio 2010 (express edition will work fine). Create a new empty website and choose a suitable name for it. Choose C# as the development language.
2) Add a new item to your site, a web form. Leave the default name, Default.aspx
3) Add a new project to your solution, a class library project.Remove the class1.cs file from the project.
4) Create a database in the instance of your SQL Server and name it CompanyEmployees . In this post you will find the SQL Script that creates a table named Employees and a table called Companies.They have various columns and they also have a one to many relationship among them (Foreign Key constraint).
5) Add a new item to your class library project, a ADO.Net Entity Data model. Choose a suitable name for it, e.g CompanyEmployees.edmx.
6) Then the Wizard pops up. Choose "Generate from Database".Choose the database which you will base the model on , CompanyEmployees.Follow exactly the steps 5-9 that you can see in this post to finish the steps of the wizard.Now you have your entity data model. Let's create a stored procedure to select some data from the Employees table.
We will have a stored procedure that takes as an input parameter the country of an employee and return information about this employee.
7) In the query window type,
USE [CompanyEmployees]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[GetEmployeesByCountry] @Country NVARCHAR(50)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON ;
SELECT emp.EmpFirstName ,
emp.EmpLastName ,
emp.Email ,
emp.City
FROM Employees emp
WHERE country = @Country
END
GO
8) Execute the T-SQL and you have the GetEmployeesByCountry stored procedure.Now we want to import this new database object into our Entity Data Model.The stored procedure will become a method in our entity data model. We have to switch to the CompEmp.edmx file and our entity designer and right click on the designer and choose "Update model from database".Select the stored procedure and click "Finish" Have a look at the picture below
9) Now we will choose Model Browser. Select Function Imports and then choose Add Function Import... and choose the stored procedure GetEmployeesByCountry.
Have a look at the picture below
We have to create a custom type-New complex type since our stored procedure does not return a whole entity.
Custom type means basically that will create a custom class with just those properties defined in the procedure/method. When you click "OK", you will have imported the procedure in the model.
Have a look at the CompEmp.Designer.cs file to see the generated code for the procedure and the complex type.
10) Let's use the stored procedure now.The main idea is to have the dropdown list control filled in with all the countries and then as the user picks countries to pass this country as a parameter to the stored procedure and bind the resultset to the Gridview control
Add a dropdown list on the Default.aspx page.Add a GridView control on the page. In the Page_Load event handling routine type,
if (!IsPostBack)
{
using (CompanyEmployeesEntities ctx = new CompanyEmployeesEntities())
{
var query = from myemp in ctx.Employees
select myemp.Country;
DropDownList1.DataSource = query;
DropDownList1.DataBind();
}
} 11) In the type DropDownList1_SelectedIndexChanged event type,
using (CompanyEmployeesEntities ctx = new CompanyEmployeesEntities())
{
var query = ctx.GetEmployeesByCountry(DropDownList1.SelectedValue.ToString());
GridView1.DataSource = query;
GridView1.DataBind();
}
12) Run your application and see all the countries in the dropdown list control. Choose one and see the employee's details for that country printed on the screen.Launch SQL Profiler and have a look at the stored procedure being called and executed.
In the following steps I will create the stored procedures I need to insert,delete,update data from the database.
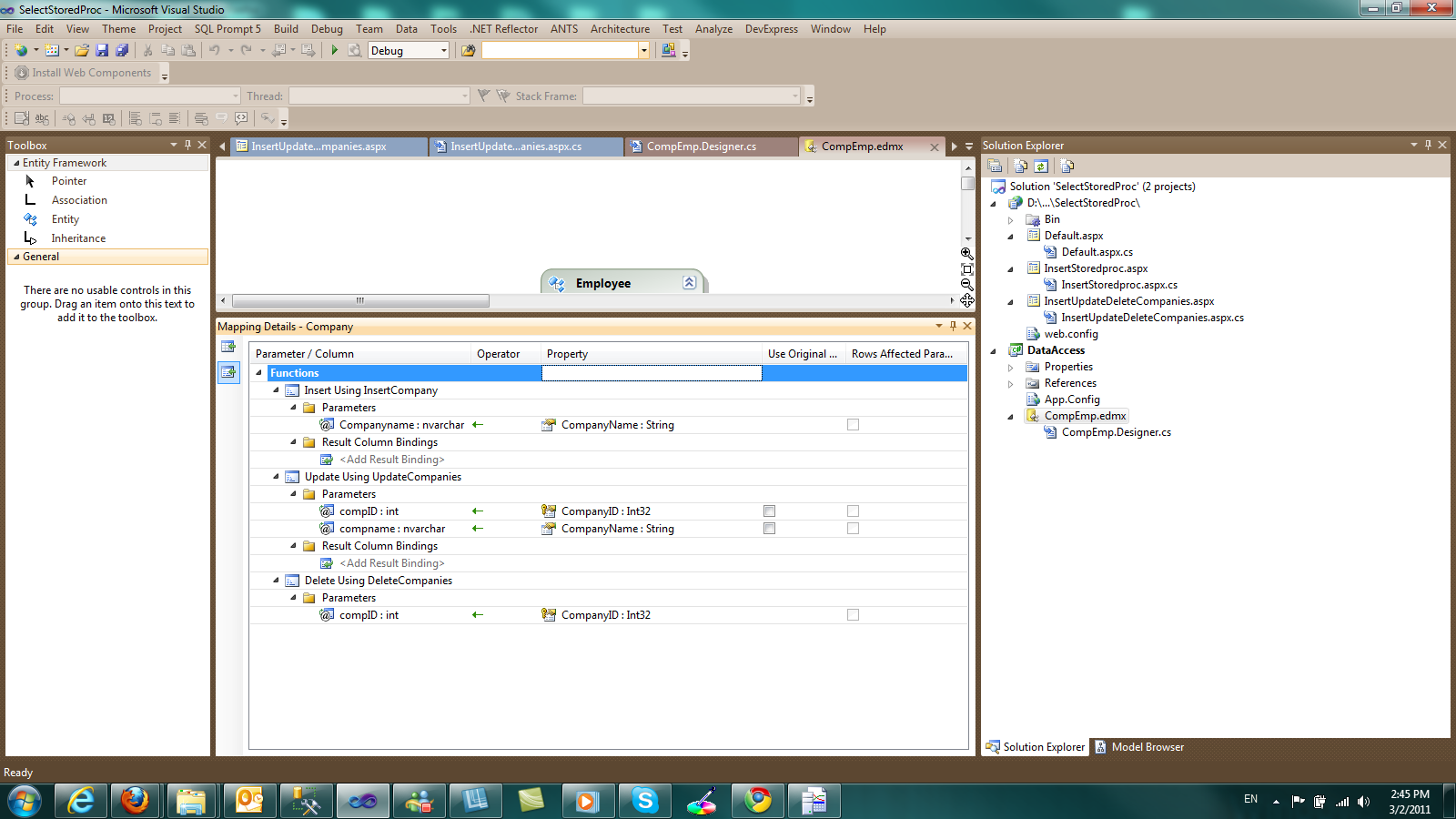
You will need to bring the stored procedures into the model by hitting "Update model from database..." . Then you will need to map those functions to the Companies entity.
We know that the EF
generates its own insert,update and delete statements. We can override
the default behaviour by mapping functions to a specific entity. We
always need to call the SaveChanges() method and the stored procedure is called instead of the native commands.
Have a look at the picture below to see the complete mapping.
13) Now we will create another stored procedure to insert a record in the Companies table.In the Query window type,
USE [CompanyEmployees]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[InsertCompany]
@Companyname NVARCHAR(50)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON ;
INSERT INTO dbo.Companies
( CompanyName )
VALUES ( @CompanyName )
END
GO
14) Add a new web form to the page.Name it StoredProcs.aspx. Add a button on the form. In the Button1_Click() event handling routine type,
try
{
using (CompanyEmployeesEntities ctx = new CompanyEmployeesEntities())
{
Company mycompany = new Company()
{
CompanyName = "Ficticious Company"
};
ctx.AddToCompanies(mycompany);
ctx.SaveChanges();
Label1.Text = "Record Inserted";
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Response.Write(ex.InnerException.Message);
}
15) Run your application and insert a new record. If you open SQL Profiler you will see that the InsertCompany stored procedure is used instead of the native sql commands.
16) Now we will create another stored procedure to update a record in the Companies table.In the Query window type,
USE [CompanyEmployees]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[UpdateCompanies]
@compID INT ,
@compname NVARCHAR(50)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON ;
UPDATE Companies
SET CompanyName = @compname
WHERE CompanyID = @compID
END
GO
17) Add a button on the form. In the Button2_Click() event handling routine type
try
{
using (CompanyEmployeesEntities ctx = new CompanyEmployeesEntities())
{
var mycompany = ctx.Companies.Where(comp => comp.CompanyName ==
"Ficticious Company").First();
mycompany.CompanyName = "My Fictitious Company";
ctx.SaveChanges();
Label1.Text = "Record Update";
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Response.Write(ex.InnerException.Message);
}
18) Run your application and update the existing record. If you open SQL Profiler you will see that the UpdateCompanies stored procedure is used instead of the native sql commands.
19) Now we will create another stored procedure to delete a record in the Companies table.In the Query window type,
USE [CompanyEmployees]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[DeleteCompanies] @compID INT
AS
BEGIN
DELETE FROM dbo.Companies
WHERE CompanyID = @compID
END
GO
20) Add a button on the form. In the Button3_Click() event handling routine type
try
{
using (CompanyEmployeesEntities ctx = new CompanyEmployeesEntities())
{
var mycompany = ctx.Companies.Where(comp => comp.CompanyID==1005)
.First();
ctx.DeleteObject(mycompany);
ctx.SaveChanges();
Label1.Text = "Record Deleted";
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Response.Write(ex.InnerException.Message);
}
21) Run your application and delete an existing record.In this sample of mine I just hard coded the CompanyID. If you open SQL Profiler you will see that the DeleteCompanies stored procedure is used instead of the native sql commands.
Drop me an email if you want the source code.
Hope it helps!!!
Comments have been disabled for this content.